FACULTY
教員紹介
FACULTY

Professor
MIURA Hiroyuki
三浦 弘之 教授
建築防災学研究室
Disaster Prevention Engineering Laboratory
専門
地震工学,防災リモートセンシング
Earthquake engineering, Remote sensing for disaster response
研究の概要説明
大地震などの広域自然災害による被害軽減を目指して、次の項目に関する研究を行っています。1. 強震記録や微動記録を用いた地盤震動特性の把握,2. 建物群の地震被害予測手法の高度化に関する研究,3. GISやリモートセンシング技術を利用した地震危険度評価・被害把握
My research interests are 1. Evaluation of Ground Motion Characteristics Based on Strong Motion and Mictotremor Data, 2. Earthquake Damage Assessment of Buildings, and 3. Spatial Data Analysis for Vulnerability and Damage Assessment.
現在の研究テーマ
・地震動評価,リモートセンシング画像への深層学習の適用
Application of deep learning for seismic motion evaluation and remote sensing analysis
研究室サイト
広大研究者総覧
研究・プロジェクト内容
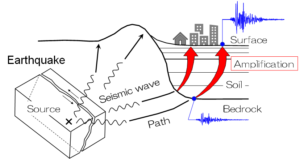
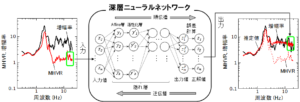
地震動予測のための深層学習の適用
大地震時における地盤の揺れを精密に予測するには,周波数(周期)ごとの揺れやすさを表す地盤増幅特性の評価が重要になります。地盤や建物は地震がなくとも微少な振幅で揺れており,微動を呼ばれています。微動はいつでもどこでも計測可能であることから,地盤や建物の振動特性の把握に利用されてきました。本研究では,AI技術のひとつである深層学習を利用して,微動データから地盤増幅特性を精度良く推定する技術の開発を行っています。
Application of deep learning for seismic motion evaluation
Evaluation of frequency (period)-dependent site amplification factor is crucial for accurately predict seismic ground motions in large earthquakes. Grounds and buildings always vibrate with very small amplitudes even without earthquake excitations. Such small vibrations have been called as microtremor, and they have been used for evaluation for vibration characteristics of grounds and buildings. In this study, we have been developing technologies for accurately evaluating site amplification factors from microtremor data using deep learning, one of the AI technologies.

災害把握のためのリモートセンシング技術の活用
自然災害が発生した場合,できるだけ迅速に被害の大きさや分布を把握することが重要になります。人工衛星,航空機,ドローンから撮影される画像は,リモートセンシングデータと呼ばれ,地表の様子を広域で一度に取得できることから,面的な被害情報を収集するのに有効です。本研究では,リモートセンシングデータを活用し,高度な画像処理技術や機械・深層学習を適用することにより,短時間・自動的に被害情報を収集する技術の開発を行っています。
Application of remote sensing technology for post-disaster response
It is important to immediately identify distributions of severities and extent of damage after natural disasters. Remotely sensed images observed from satellites, aircrafts and UAVs has been recognized as a useful tool for assessing damage maps affected by the disasters. In this study, we have been developing technologies for fast and automatic estimations of damage information from remote sensing data by applying advanced image processing and machine/deep learning.